Inkha Electronics Hardware
current requirements
current requirements of the hitec servos chosen for neck movement and mouth were found from manufacturer’s data sheets (see data sheets section)
current requirements of the cirrus servos supplied with the eye assembly could not be found from the manufacturer and were estimated from a hitec servo with similar torque output
this gave total servo current requirements as follows:
| Servo | Current (mA) | Voltage (v) |
| eye pitch | 280 | 4.8 – 6 |
| left eye yaw | 280 | 4.8 – 6 |
| right eye yaw | 280 | 4.8 – 6 |
| left eyelid | 280 | 4.8 - 6 |
| right eyelid | 280 | 4.8 - 6 |
| neck yaw | 700 | 4.8 - 6 |
| neck top pitch | 300 | 4.8 - 6 |
| neck bottom pitch | 300 | 4.8 - 6 |
| mouth | 180 | 4.8 - 6 |
| total | 2880 |
on request seetron quoted a 4 amp rating for the mini ssc servo controller board
current requirements for other electrical components were as follows:
| component | current (ma) | voltage (v) |
| mini ssc | 10 | 7 - 15 |
| autotalk | 20 | 5 - 6 |
| camera (2) | 100 | 6 - 12 |
| pir (2) | 24 | 7.5 - 12 |
| total | 154 |
interference
initial tests running the eye mechanism and the cameras
concurrently showed that servo movement caused interference on the camera signal
experiments showed that using a secondary power supply for the cameras avoided this
problem
although the cameras are specified as requiring 12v they run perfectly well at voltages
down to 7.5v
this also allowed one power supply to be run at 6v for the servos and and one at 7.5v for
the cameras and all other components
power supplies
the maximum theoretical current requirement for the servos
calculated above is 2.9a
in practice the servos are not powered simultaneously so the power supply only has to be
large enough to power the largest servo with a safety margin
following recommendations in seetron user manual two 1.2a linear regulated power supplies
were purchased from maplin, one running at 6v for the servos and one at 7.5v for the other
electronic components
autotalk board
the mini ssc servo controller supplied with the eye
assembly had three spare servo outputs which were required to run the neck servos
to avoid the need for a second servo controller an autotalk board was purchased from
milford instruments which drives a servo motor in synchronisation with audio input
a data sheet for the autotalk board can be found in the data
sheets section
one disadvantage of this board is that it cuts out any audio output from the computer so a
set of dedicated amplified speakers was also bought from maplin
secondly the gain was insufficient to move the featherservo the required range
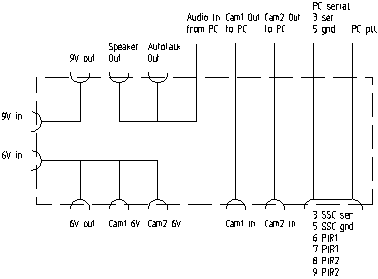
interface box
the interface box was designed to use
different connectors for each unique signal to avoid any ambiguity when connecting to it
a schematic of the connections between the sockets is as follows:
relay box
the relay box is used optionally for
unattended running
it uses a card from audon technologies
which allows relays to be controlled from the parallel port
one of these relays is wired in series with the low voltage side of the motor power supply
unit
the effect of this is that inkha's motors can be turned off under program control
the control system turns the motors off whenever inkha goes to sleep which saves them from
burnout caused by continuous running
there are some security issues involved with
controlling a parallel port under windows nt and later and a windows driver and code from sst was used to overcome this